The Fluvio CLI (command-line interface) is an all-in-one tool for setting up, interacting, and managing with Fluvio clusters.
Install the Fluvio CLI by running the following command:
$ curl -fsS https://hub.infinyon.cloud/install/install.sh | bash
helm and kubectl are also required but installing Rancher Desktop provide access to them.
If you have Rancher Desktop already set up, then continue to steps for running a local Fluvio cluster.
Rancher Desktop is a tool for running a local Kubernetes cluster.
In order to install Rancher Desktop go to the Rancher Desktop installation page and follow the instructions. Rancher Desktop will provide access to other utilities needed to run Fluvio such as kubectl and helm.
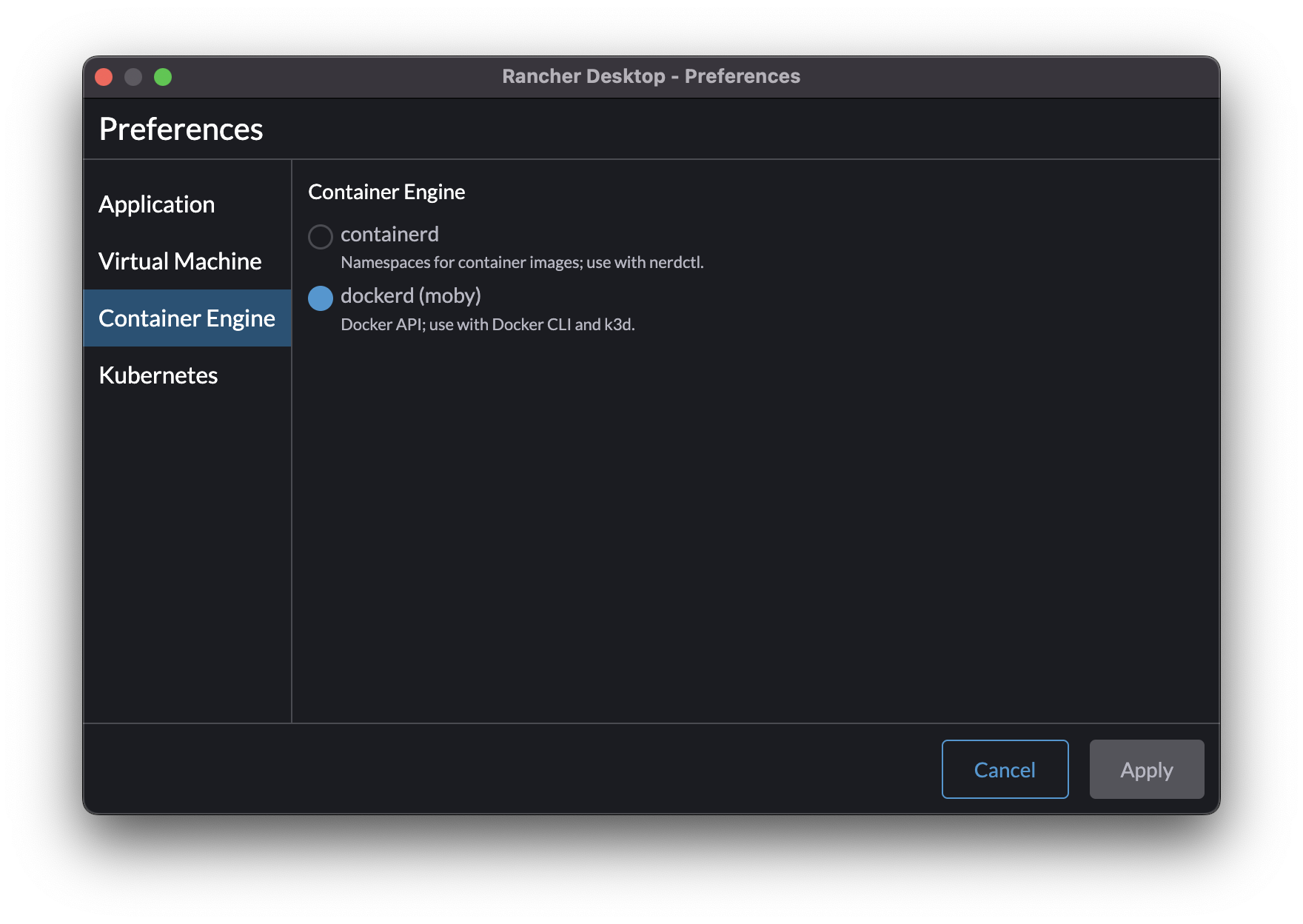
Please make sure that the container runtime is dockerd (moby). That configuration can be changed in the Kubernetes Settings section on the sidebar.
You can start a Fluvio cluster by running fluvio cluster start.
$ fluvio cluster start
We can check the fluvio cluster by checking version and status with the following command:
$ fluvio version
Release Channel : stable
Fluvio CLI : 0.9.31
Fluvio CLI SHA256 : aa2c91656c492cbb2700fca622633bc4ad03b64d8a45ba0f2b39ed0c05ca84b0
Fluvio channel frontend SHA256 : 068b910b0082ec30fcb9ae210d8f73f3109ca3fe854b6f7864992f5b7524bd82
Fluvio Platform : 0.9.31 (rancher-desktop)
Git Commit : e9cf0a7e2096758dc37031ea2d99023b4b968182
OS Details : Darwin 12.4 (kernel 21.5.0)
=== Plugin Versions ===
Fluvio Runner (fluvio-run) : 0.0.0
Infinyon Cloud CLI (fluvio-cloud) : 0.1.8
Congratulations, you’ve successfully installed Fluvio on your local machine!
Let’s use the Fluvio CLI to play with some basic functionality.
The first thing we need to do is create a topic.
$ fluvio topic create greetings
topic "greetings" created
Now that we have a topic, we can produce some messages!
Use the following command to send a message to the greetings topic:
$ echo "Hello, Fluvio" | fluvio produce greetings
Finally, we can consume messages back from the topic
$ fluvio consume greetings -B -d
Consuming records from the beginning of topic 'greetings'
Hello, Fluvio
Way to go! You’re well on your way to writing real-time distributed apps with Fluvio!
If you run into any problems along the way, make sure to check out our troubleshooting page to find a fix.